
Rainscreen Facade Systems: Structure, Applications, and Types
2024/10/29The Rainscreen Facade System, as one of the most innovative and advanced methods for building facades, has garnered significant attention from architects and engineers in recent years. This system not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of a building but also improves its performance in thermal and acoustic insulation, moisture control, and durability, making it an ideal choice for modern buildings.
In this article, a comprehensive examination of Rainscreen facade systems is presented, addressing fundamental questions regarding their structure, advantages, applications, and various types. If you do not find answers to your questions at the end of this article, please be sure to contact the Research and Development Department of Alum Gostar.
What is a Rainscreen Facade System?
The Rainscreen Facade System is an exterior cladding system in which the outer layer of the facade is separated from the inner layer, creating a cavity between them. This cavity acts as a ventilated space, allowing moisture and air to easily pass behind the facade. In simpler terms, the rainscreen facade system acts like a protective curtain that prevents direct water infiltration into the building while allowing the facade to “breathe.” This system not only improves the thermal and acoustic performance of the building but also significantly enhances the durability and lifespan of the facade.
The history of using similar systems to rainscreens dates back centuries. In traditional architecture across many cultures, various methods were employed to create a gap between the outer and inner layers of the facade. However, the modern concept of the rainscreen facade system and its widespread use in contemporary buildings has emerged in recent decades. With advancements in construction technologies and increased awareness of the importance of energy performance in buildings, rainscreen systems have become an efficient and sustainable solution for building facades.
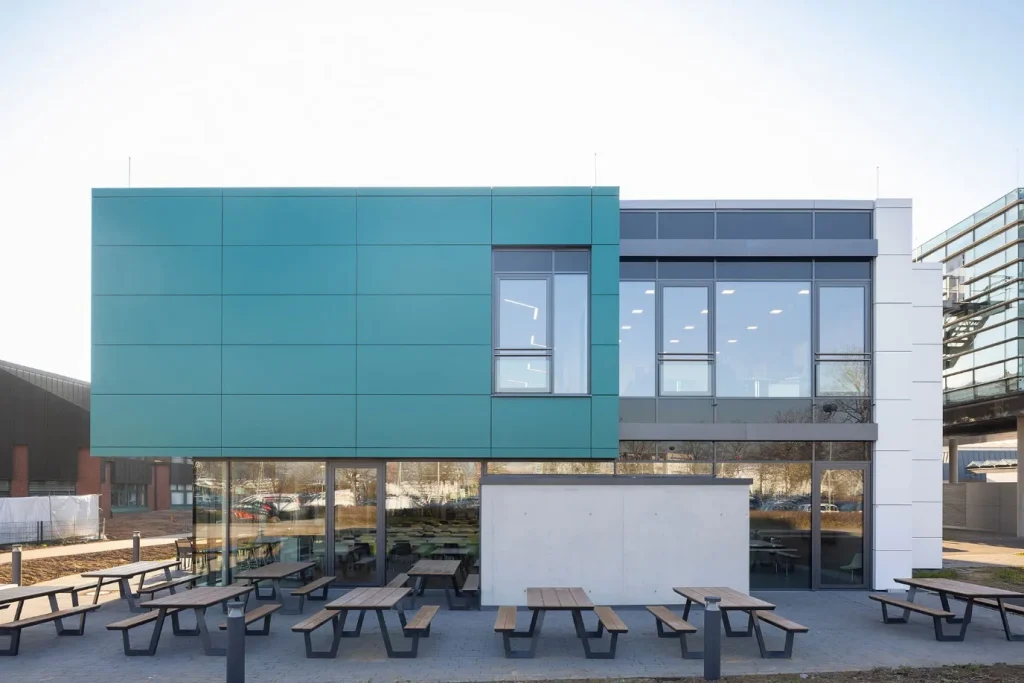

Structure of Rainscreen Facade Systems
The Rainscreen Facade System consists of several distinct layers, each playing a crucial role in the overall performance of the system. The outer layer serves as a protective shell, shielding the building from weather elements such as rain, wind, and sunlight. In addition to its aesthetic appeal, this layer acts as a barrier against air pollution.
Behind the outer layer, there is a cavity that functions as a ventilated space. This space allows air to flow freely behind the facade and helps remove moisture from the surface. The presence of this cavity prevents moisture buildup and the growth of mold and mildew behind the facade, contributing to the building’s durability.
The inner layer of the rainscreen facade system is typically made of a waterproof membrane that prevents water from penetrating into the building. This membrane acts as an additional protective layer, safeguarding the thermal insulation and structural elements from moisture damage.
The materials used in the construction of Rainscreen systems are highly diverse and can vary based on the type of building, climatic conditions, and the designer’s preferences. Metals such as aluminum, corrosion-resistant steel, and copper are popular choices for the outer layer due to their high resistance to corrosion and variety in colors and designs. Glass can also be used for its beauty and transparency; however, when glass is used as the outer shell of a rainscreen, light transmission through the glass is often disregarded, and spandrel glass is commonly employed in these cases. Composite materials such as aluminum and fiberglass composites are also suitable options due to their lightweight and high durability.

Advantages of Using Rainscreen Systems in Buildings
The Rainscreen Facade System has become one of the most popular cladding methods for modern buildings due to its numerous advantages and outstanding performance. This system provides innovative and efficient solutions, significantly enhancing the building’s performance in various areas. Below are some of the most important advantages of using a rainscreen facade system:
- Prevention of Moisture and Water Infiltration: By creating an air gap between the outer and inner layers of the facade, it prevents moisture and water from entering the building, thereby avoiding damage caused by humidity.
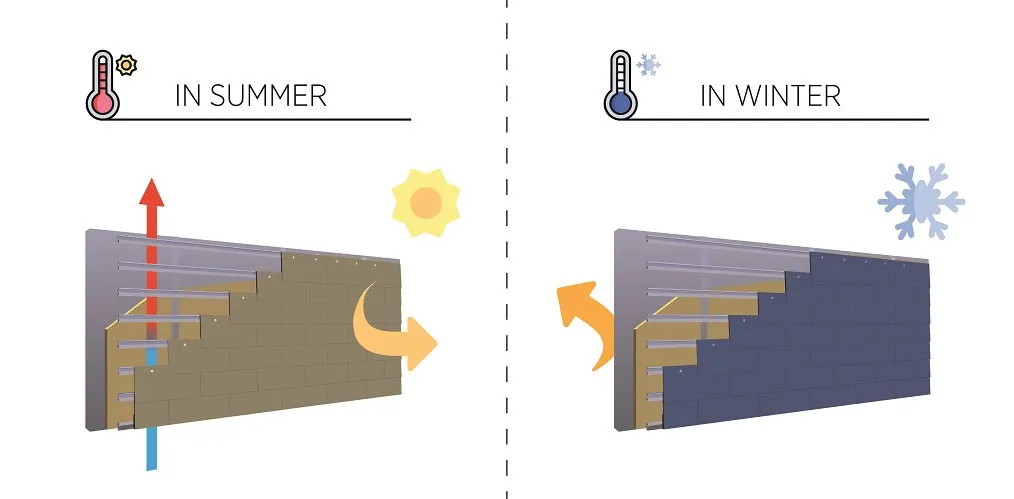
- Improved Thermal Performance: These systems act as thermal insulation, reducing energy loss in cold seasons and limiting heat gain in warm seasons.
- High Durability and Longevity: The materials used in these systems are highly resistant to weather elements, thus increasing the useful life of the building.
- Flexibility in Modern Designs: The wide variety of materials and designs allows for the creation of beautiful and modern facades with a high degree of customization.
Applications of Rainscreen Facade Systems
The Rainscreen Facade System, due to its numerous advantages, is used in various types of buildings. This system’s high flexibility and adaptability to different conditions make it applicable in a variety of construction projects. Below are some of the most important applications:
Application in Residential Buildings
The use of the Rainscreen Facade System in residential buildings is very popular due to its aesthetic appeal, high durability, and improved thermal performance. This facade system allows residents to enjoy a comfortable indoor environment. Additionally, the ability to use diverse designs and various colors in the facade enables residents to customize the appearance of their building according to their personal preferences.
Application in Commercial and Office Buildings
In commercial and office buildings, the Rainscreen System is highly regarded for creating a modern and attractive facade, improving the building’s energy performance, and enhancing the durability of the facade. This facade gives commercial and office buildings identity and character, contributing to the overall appearance of the structure.
Application in Different Climatic Zones
The Rainscreen Facade System is suitable for use in various climatic zones due to its high resistance to weather elements. These systems are particularly beneficial in areas with heavy rainfall, such as coastal regions and humid climates, as they prevent direct water infiltration into the building, protecting the structure and prolonging its lifespan. Additionally, in areas with significant temperature variations, the rainscreen facade provides an insulating air layer that helps reduce energy loss, contributing to lower heating and cooling costs for the building.

Types of Rainscreen Facade Systems
The Rainscreen Facade System is designed and produced in various types, each with its own specific features and applications. Below, we will examine some of the common types of these systems.
Open and Closed Rainscreen Facade
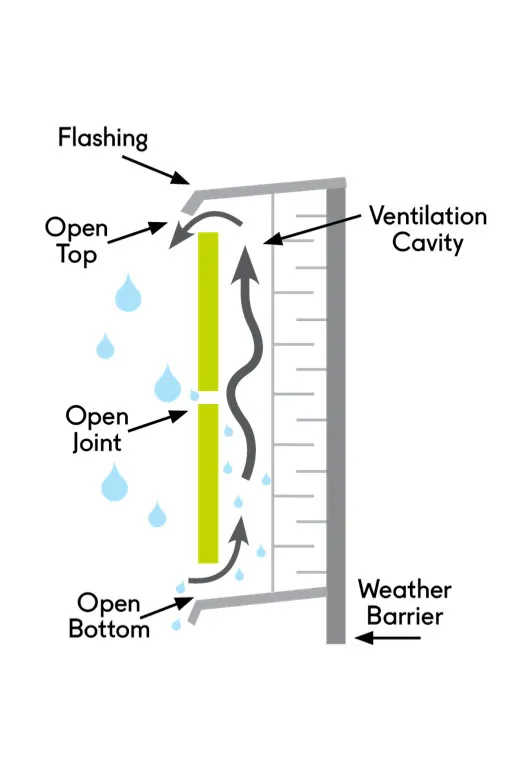
These systems are divided into two main categories—open and closed—based on the degree of openness of the space between the outer and inner layers. In the open rainscreen facade system, this space is completely open, allowing air to easily pass through. This enhances ventilation behind the facade and prevents moisture buildup and the growth of mold and mildew. As a result, the durability and lifespan of the building are increased, and problems caused by moisture, such as metal corrosion and wood decay, are avoided.
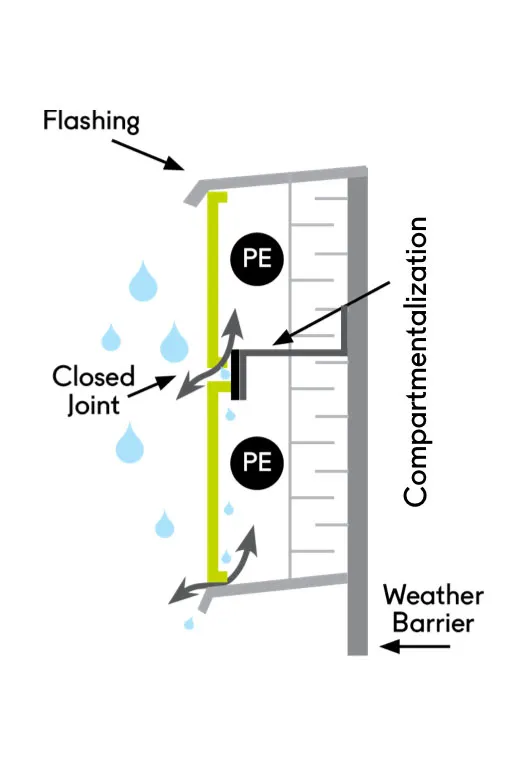
In contrast, in closed systems, the space between the layers is partially obstructed, and air can pass through it only to a limited extent. These types of systems are typically used in cold and dry climates, as they reduce heat loss by limiting airflow. However, closed systems are more prone to moisture buildup due to less ventilation compared to open systems, and therefore require more maintenance.
Ventilated and Non-Ventilated Systems
Rainscreen facade systems can be divided into two main categories based on the presence or absence of a mechanical ventilation system. In ventilated rainscreen systems, an active mechanical ventilation system draws air from behind the facade and directs it outside. The main advantage of this system is the creation of a controlled environment with better indoor air quality.
In contrast, non-ventilated systems are not equipped with mechanical ventilation, and air circulation occurs naturally through air pressure differences. These systems are simpler and cheaper than ventilated systems and can be used in buildings that do not require extensive air ventilation.
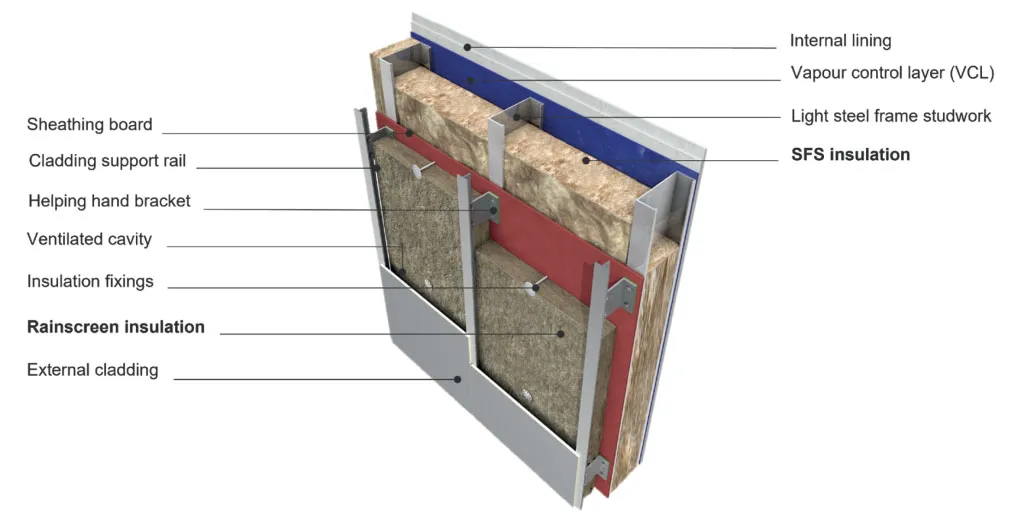
Rainscreen Systems with Additional Protective Layers
Some rainscreen systems feature additional protective layers, such as sound insulation or thermal insulation. These layers help improve the system’s performance in reducing noise pollution and decreasing energy consumption.
Comparison of Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Types of Rainscreen Systems
The choice of the appropriate type of Rainscreen System depends on various factors. Each type of rainscreen system has its own specific advantages and disadvantages. For example, the open rainscreen facade offers better ventilation but is more sensitive to dust infiltration. In contrast, closed systems provide better insulation but have less ventilation. To select the best type of system, various factors such as the building’s usage, climatic conditions, budget, and specific project requirements must be considered.
How to Choose the Best Rainscreen System for a Building?
Choosing the most suitable Rainscreen System for a building requires a thorough and comprehensive examination of various factors. This choice will directly impact the building’s performance, durability, and aesthetics. Some of the most important considerations when selecting a rainscreen facade system include:
- Examination of Climatic Conditions: The type of system should be compatible with the climatic conditions of the area. For regions with heavy rainfall and high humidity, open systems with adequate ventilation are recommended. In contrast, in dry and cold areas, closed systems with better thermal insulation may be more suitable.
- Economic Considerations: The cost of Rainscreen systems depends on various factors, such as the type of materials, design complexity, and the dimensions of the building. Before selecting a system, it is important to establish the budget and then compare the available options based on that budget.
- Aesthetic Needs Assessment: In addition to technical performance, the rainscreen facade must align with the overall design of the building and its surroundings. Therefore, before choosing a system, personal preferences, the architectural style of the building, and urban planning regulations should be taken into account.

Installation and Execution Steps of the Rainscreen Facade System
The installation and execution of this system is a precise and specialized process that requires adherence to technical and engineering principles. This process generally includes the following main steps:
Preparing the Infrastructure
The first step in the installation is preparing the building’s infrastructure. This stage includes a thorough assessment of the existing facade conditions, repairing and restoring damaged areas, installing thermal and acoustic insulation, and setting up a support structure to hold the rainscreen panels. Properly preparing the infrastructure ensures the correct functioning and longevity of the system over time.
Installing Protective Layers and Ventilation Systems
After preparing the infrastructure, the next step is to install the protective layers and ventilation systems. Protective layers such as waterproofing, thermal insulation, and sound insulation are installed on the infrastructure to prevent moisture, cold, heat, and sound from penetrating the building. Additionally, the ventilation systems are installed at this stage to ensure proper airflow behind the facade and prevent moisture buildup.
Methods for Connecting and Installing Rainscreen Panels
In the final stage, the rainscreen panels are installed on the support structure. The methods for attaching the panels to the support structure vary and are chosen based on the type of panel and project conditions. Common methods of attachment include the use of screws and anchors, specialized adhesives, and hanging systems. It is also important to pay close attention to sealing the joints accurately to prevent water infiltration behind the facade.
Conclusion
Rainscreen facade systems have become one of the most innovative and efficient methods for cladding buildings, garnering widespread attention in recent years. The numerous advantages of these systems, including high durability, aesthetic appeal, reduced energy consumption, and improved building performance, make them an ideal choice for modern constructions. With advancements in technology and increased awareness of the importance of energy efficiency, the use of rainscreen systems is expected to continue to grow in the future. New innovations in raw materials, design, and production of these systems will enable the creation of facades with better performance and more complex designs. If you are looking for a beautiful, durable, and efficient facade for your building, using Rainscreen systems could be a highly suitable choice. For more information and advice on selecting and installing rainscreen systems,
you can consult the experts at Alum Gostar.

